Qualifications Explained
The types of qualifications available across all industries can be quite bewildering, with different levels, awards, certificates, diplomas and degrees, NVQ’s vocational qualifications and others, it’s easy to get confused. Typically, qualifications are ordered by their size i.e. how long they take to complete and their difficulty i.e. how hard they are to do.
In this resource we are going to look at the different types of some of the more common qualifications, the different levels of qualification and at what point they typically fall in some ones’ career/life.
Qualification Size
The size of the qualification determines whether the qualification is known as an award, certificate or diploma.
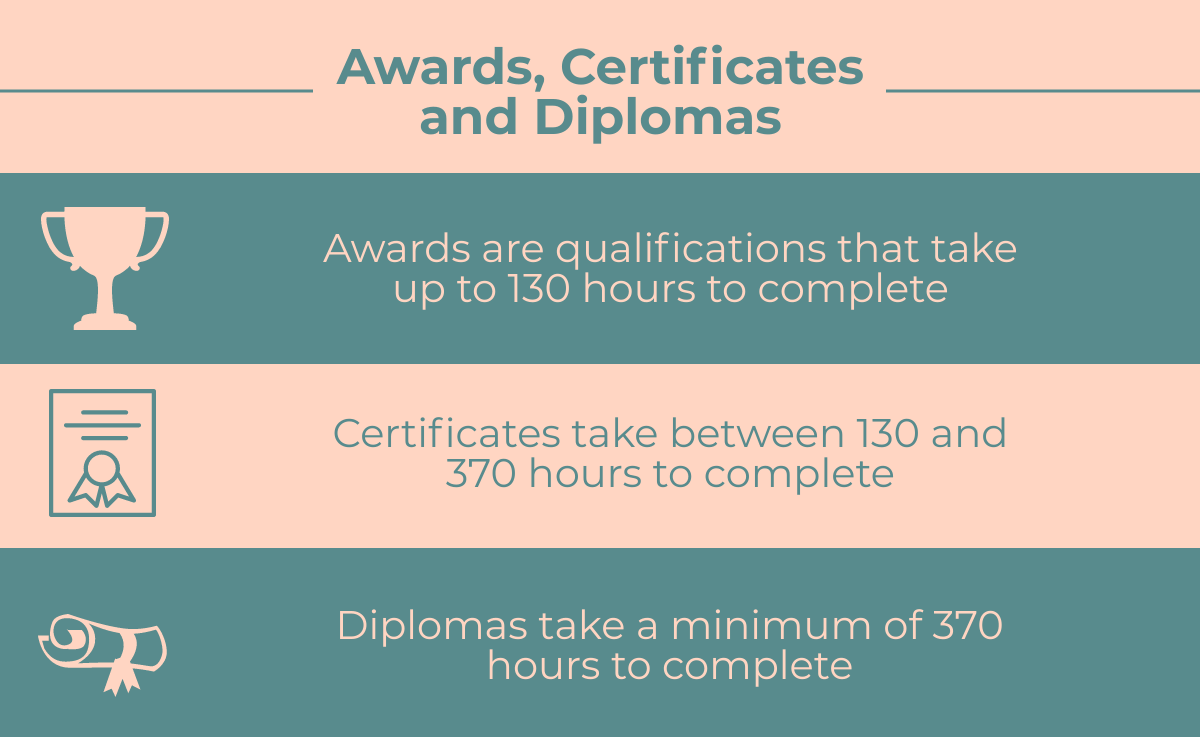
Award
Awards typically have guided learning hours of less than 130 hours. A City and Guilds Level 2 award in Fundamental Inspection and Testing for example has a 30-35 guided learning hours.
Certificate
Certificates have guided learning hours of between 130 and 370 hours. EAL’s Level 3 Certificate in Installing, Testing and Ensuring Compliance of Electrical Installations in Dwellings has 224 guided learning hours.
Diploma
Diplomas have guided learning hours of over 370. The City and Guilds 2365 Level 2 Diploma in Electrical Installations for example has 454 guided learning hours.
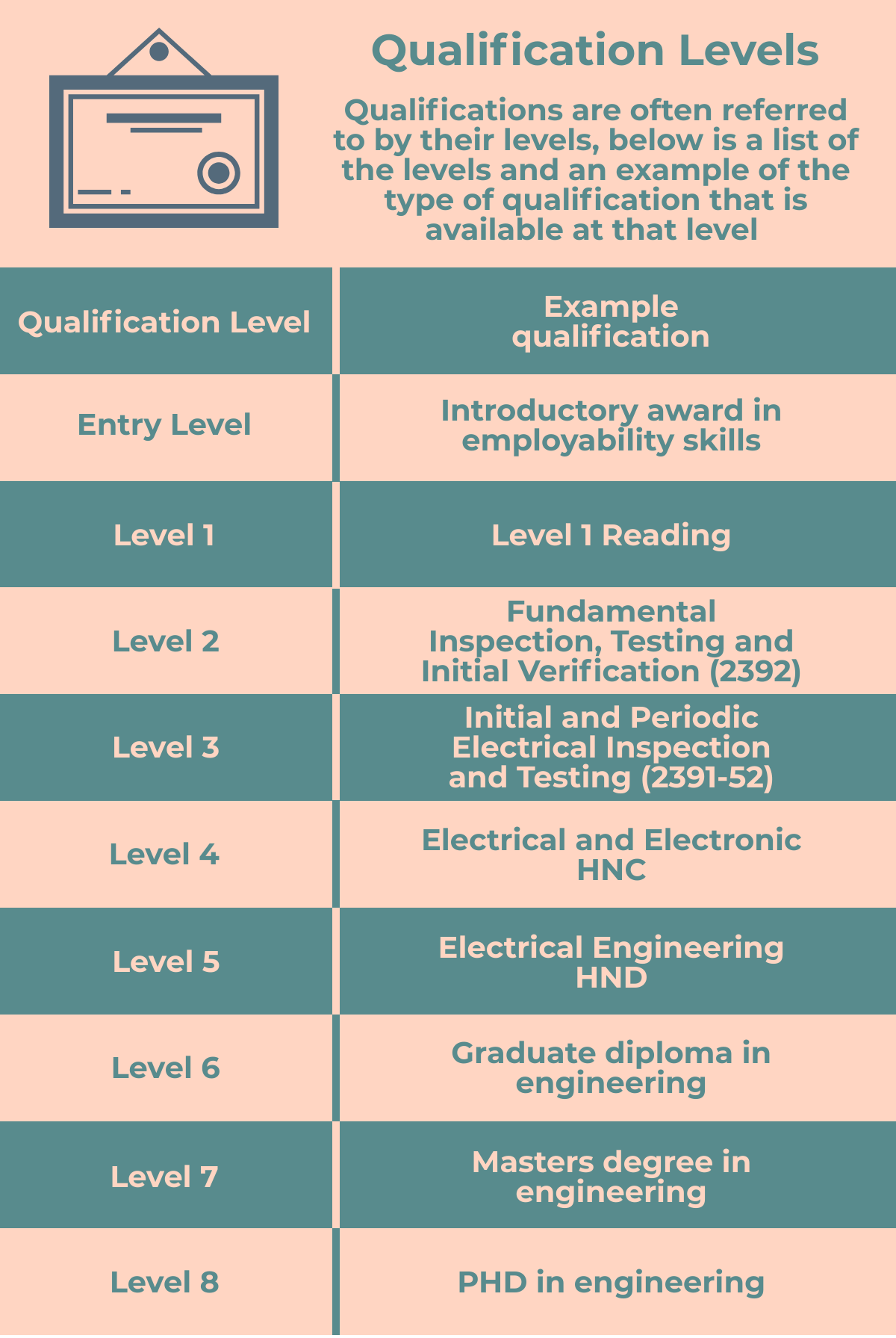
Qualification Level
The level the qualification is given denotes its difficulty. The levels are ranked on a scale from 1 to 8, with 1 being the lowest ranked and 8 being the highest ranked. Generally, the title of the qualification. A City and Guilds 2391-52 Level 3 Award in Inspection and Testing is pretty self-explanatory as to what level it sits at. However not all qualifications are this straight forward with some such as GCSE’s bridging levels.
Generally speaking, the longer qualifications give much broader coverage of a subject. The Level 2 2365 mentioned above covers topics as diverse as how to communicate with others in the workplace and the basic principles of electrical science. The 2391-52 on the on the other hand focusses purely on inspection, testing and periodic inspection and testing over a much shorter time period, but at a higher level as it is a level 3 qualification.
Types of Qualification
In this next section we are going to cover some of the more common qualifications and how they work.
GCSE’s
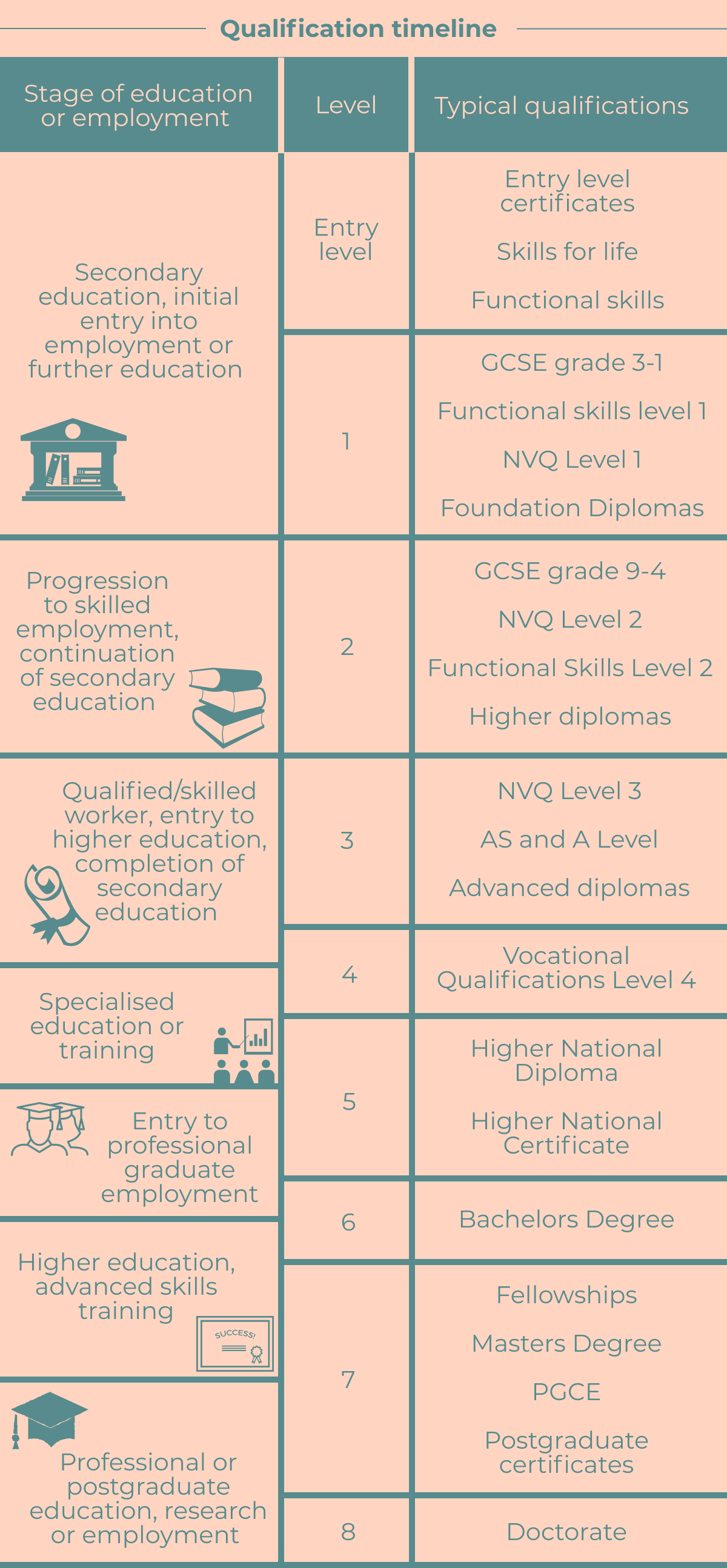
General Certificates of Secondary Education or GCSE’s for short should be familiar to the majority of people who have attended secondary school in England or Wales. They are available in wide range of subjects including applied (work related) and academic. Typically, they are taken between the ages of 14-16. A GCSE will normally take around 120 hours to complete. GCSE’s are graded on a scale from 1-9 with 9 being the highest. A GCSE graded between 1-3 would be classed as a level 1 qualification, a GCSE graded 4-9 would be classed as a level 2 qualification.
A Levels
A Levels are Advanced Level qualifications typically taking 360 hours to complete. Generally aimed at students over the age of 16, they are a prerequisite for higher education. They are a level 3 qualification.
Bachelor’s degree
Bachelor’s degrees take between 3-4 years to complete on average. The degree itself is a level 6 qualification but will teach through levels 4 and 5 as well.
Masters degrees
Masters degrees are available in many different formats and attained in many different ways depending on the subject being studied or the industry the degree pertains to. Some are integrated over a four-year period, with the first three years being spent studying at a bachelor’s level. More typically they are a postgraduate degree taken after having completed a bachelor’s degree. They tend to be very demanding and are classed as level 7 qualifications.
Doctoral degrees
Doctoral degrees are research degrees in which the candidate submits their research or thesis and then defends it. Doctoral degrees take around 3 years on average to complete. They are a level 8 qualification.
BTEC’s
BTEC stands for the Business and Technology Education Council. They are work related qualifications made up of practical and theory work. They tend not to be job specific unlike an NVQ and are available as certificates or diplomas depending on their length. BTECs are available at levels 2 to 5.
HNC’s and HND’s
Higher National Certificates (HNC) and Higher National Diplomas (HND) are vocational qualifications that are mainly offered for more practical industries such as agriculture or engineering. A HNC is a level 4 qualification and the HND is a level 5 qualification.
NVQ’s
National Vocational Qualifications (NVQ’s) are work based, practical qualifications. They are made up of mixture of education in a formal setting and work based experience. Competency is assessed through a combination of written, multiple choice, a portfolio of evidence and witnessed practical assessments. NVQ’s are available at five levels from 1 to 5. Annoyingly they don’t map directly across to the same levels as other qualifications. An NVQ Level 4 for example can be a level 4, 5 or 6 qualification, whilst an NVQ Level 3 in Electrical Installations is a level 3 qualification. The time taken to complete an NVQ varies depending on the level and subject matter, but a typical NVQ level 3 takes 3 to 4 years to complete.
Electrical Qualifications
Listed below are the more common electrical qualifications;
City and Guilds Level 3 Award in Requirements for Electrical Installations 2382
More commonly known by the edition of the wiring regulations it is based on (i.e. 18th edition) This qualification is designed to demonstrate that you are capable of understanding the requirements of the wiring regulations. Generally, a theory based course that takes place over 3-5 days with a multiple choice open book exam that needs to be successfully passed to complete the qualification.
City and Guilds Level 3 Award in the Building Regulations for Electrical Installations in Dwellings 2393
Often referred to as the ‘part-p qualification’ this qualification covers the requirements and compliance of any electrical work carried out in a dwelling. Another theory based course taken over 1-2 days. Again an open book online multiple choice exam needs to be completed successfully to gain the qualification.
City and Guilds Level 2 Award in Fundamental Inspection, Testing and Initial Verification 2392
This qualification is an entry level qualification that teaches you how to test and inspect electrical installations. The typical types of installations covered are single phase installations up to 100A, i.e. houses and flats. Taught as a combination of theory and practical work over 5 days, to successfully achieve this qualification an online exam and a practical assessment must be passed.
City and Guilds Level 3 Award in Initial and Periodic Inspection and Testing 2391-52
A Level 3 award which assesses the candidate’s ability to carry out initial verification on electrical systems (single and three phase, domestic and commercial/industrial) and complete periodic inspection and testing on the same. To achieve this qualification, you have to successfully pass two practical assessments, a written assessment and an online multiple choice assessment.
City and Guilds Level 2/3 Diploma in Electrical Installations (Building and Structures) 2365-02 and 2365-03
The 2365 is a qualification that’s designed as the foundation before progressing onto the Level 3 NVQ. It covers electrical installation in depth from a theory standpoint. It is available at Levels 2 and 3. As a purely theory based qualification it allows people to take it without having to gain on the job experience as they would in an NVQ.
City and Guilds Level 3 NVQ Diploma in Installing Electrotechnical Systems and Equipment (Buildings, Structures and the Environment) 2357-13
This qualification allows the candidate to demonstrate that they have achieved the required competence to carry out installation work. The majority of this qualification consists of completing a portfolio of evidence demonstrating that all the required competencies have been met.
City and Guilds Level 3 Electrotechnical Apprenticeship Qualification 5357
As the name suggests, this qualification is designed for candidates who are entering into an apprenticeship within the electrical industry.
Want to find out exactly how to become an electrician? Take a look at all of the electrician courses we offer!